Customer engagement is constantly evolving and the trend towards more customer-centric experiences hasn’t slowed. Businesses are increasingly having to provide faster, easier, and more friendly ways of initiating and responding to customer’s inquiries.
Businesses that adapt to this continually changing environment will ensure they deliver superior service along with desirable products, thus boosting engagement rates.
This is where customer engagement strategies based on text messaging enter the picture. This mode of communication has overtaken traditional methods, like phone and email, as consumers prefer the ease, convenience, and hassle-free nature of text messaging.
Texting isn’t just for friends and family anymore and consumers are choosing this channel more often as it fits their on-the-go lifestyle.
The move to text messaging is a part of this new era of building customer relationships, and both businesses and consumers can benefit.
The old customer engagement marketing strategies are fading
As recently as two decades ago, the world of business and customer service was a completely different place. Company agents and representatives used forms of customer engagement like trade shows, promotional emails, letters, and phone calls to promote their products and services.
While these methods are still used in a wide range of industries, many companies today are turning to new ways of maintaining customer loyalty.
According to the Pew Research Center, about 96% of Americans own a cell phone of some kind. Text messaging is a highly popular form of communication in people’s everyday lives. As such, it only seems natural that companies would use texting as a service, sales, and marketing tool. Their results have been astounding, and that’s what we’ll explore in the next section.
The advantages of digital customer engagement strategies
While sending text messages to customers may be a new frontier for many companies, businesses are finding the personal, casual nature of this medium is part of what makes it so effective.
Some of the benefits that come with text-based customer service include:
Hassle-free customer service access
Consumers love instant messaging because it’s easy and allows them to engage, ask questions, and get information without having to make a phone call or meet face-to-face.
One of the hallmarks of our increasingly digital world is how hard businesses work to make things easy – think of 1-click shopping on Amazon (you don’t have to click two buttons), how smartphones enable contactless payment (you don’t have to pull your card out), the way Alexa responds to voice commands (you don’t have to click anything), and the way Netflix automatically plays the next episode of a show you’re binging (you don’t even have to move).
These expectations are becoming more ingrained in the minds of consumers, especially young ones, and they are unlikely to be enthusiastic about needing to call an agent or go into the store to resolve any problems they have.
Timely responses and service
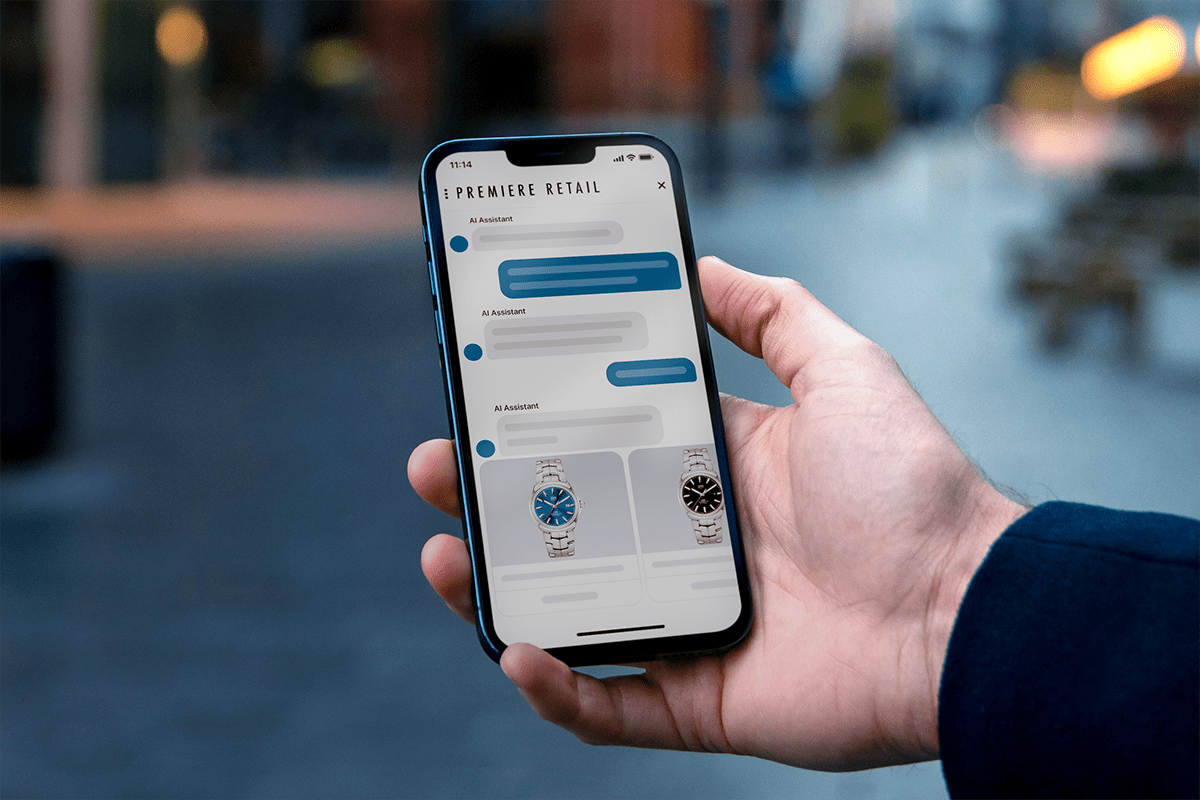
Few things turn a customer off faster than sending an email or making a phone call, then having to wait days for a response. With text message customer service, you can stay connected 24/7 and provide timely responses and solutions. Artificial intelligence is one customer engagement technology that will make this even easier in the years ahead (more on this below).
The personal touch
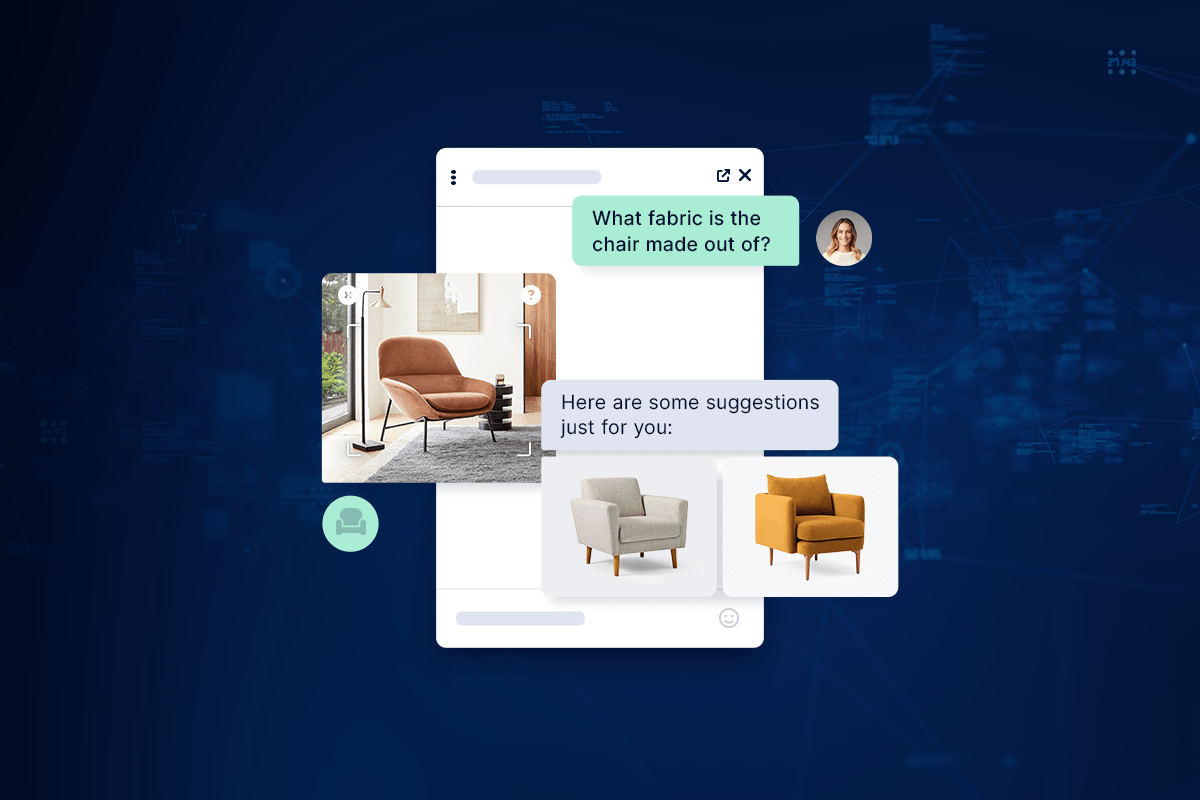
Customers are more likely to stick around if they believe you care about their personal needs. Texting will allow you to take a more individualized approach, communicating with customers in the same way they might communicate with friends. This stands in contrast to the stiffer, more formal sorts of interactions that tend to happen over the phone or in person.
A dynamic variety of solutions
Text messaging provides unique opportunities for marketing, sales, and customer support. For example, you might use texting to help troubleshoot a product, promote new sales, send coupons, and more.
None of these things are impossible to do with older approaches to customer service but think of how pain-free it would be for a busy single mom to ask a question, check the reply when she stops to pick up her daughter from school, ask another question, check the new reply when she gets home, etc. This is vastly easier than finding a way to carve three hours out of the day to go into the store to speak to an agent directly.
To make these ideas easier to digest, here is a table summarizing the ground we’ve just covered:
| The Old Way | The New Way | |
| Method of Delivery | Phone calls, pamphlets, trade shows, face-to-face conversations | Text messaging |
| Difficulty | Requires spending time on the phone, driving to a physical location, or making an appointment. | Only requires a phone and the ability to text on it. |
| Timeliness | Can take hours or days to get a reply. | Replies should be almost instantaneous. |
| Personalization | Good agents might be able to personalize the interaction, but it’s more difficult. | Personalizing messages and meeting a customer on their own terms because natural and easy. |
| Variety | Does offer ways of solving problems or upselling customers, but only at the cost of more effort from the agent. | Sales and customer support can be embedded seamlessly in existing conversations, and those conversations fit better into a busy modern lifestyle. |
Why this all matters
These benefits matter because 64% of Americans would rather receive a text than a phone call. It’s clear what the consumers want, and it’s the business’s job to deliver.
Because text messaging can help you engage with customers on a more personal level, it can increase customer loyalty, lead to more conversions, and in general boost engagement rates.
What’s more, text-based customer relationships will likely be transformed by the advent of generative artificial intelligence, especially large language models (LLMs). This technology will make it so easy to offer 24/7 availability that everyone will take it for granted, to say nothing of how it can personalize replies based on customer-specific data, translate between languages, answer questions in different levels of detail, etc.
Texting already provides agents with the ability to manage multiple customers at a time, but they’ll be able to accommodate far higher volumes when they’re working alongside machines, boosting efficiency and saving huge amounts of time.
Some day soon, businesses will look back on the days when human beings had to do all of this with a sense of gratitude for how technology has streamlined the process of delivering a top-shelf customer experience.
And it is exactly this customer satisfaction that’ll allow those businesses to increase profits and make room for business growth over time.
Request a demo from Quiq today
In the future, as in the past, customer service will change with the rise of new technologies and strategies. If you don’t want to be left behind, contact Quiq today for a demo.
We not only make it easy to integrate text messaging into your broader approach to building customer relationships, we also have bleeding-edge language models that will allow you to automate substantial parts of your workflow.