In Part One of this guide, we explored the foundational architecture needed to build production-ready AI agents – from cognitive design principles to data preparation strategies. Now, we’ll move from theory to implementation, diving deep into the technical components that bring these architectural principles to life when you attempt to build your own AI assistant or agent.
Building on those foundations, we’ll examine the practical challenges of natural language understanding, response generation, and knowledge integration. We’ll also explore the critical role of observability and testing in maintaining reliable AI systems, before concluding with advanced agent behaviors that separate exceptional implementations from basic chatbots.
Whether you’re implementing your first AI assistant or optimizing existing systems, these practical insights will help you create more sophisticated, reliable, and maintainable AI agents.
Section 1: Natural Language Understanding Implementation
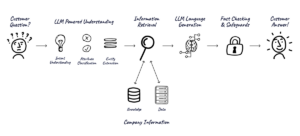
With well-prepared data in place, we can focus on one of the most challenging aspects of agentic AI agent development: understanding user intent. While LLMs have impressive language capabilities, translating user input into actionable understanding requires careful implementation of several key components.
While we use terms like ‘natural language understanding’ and ‘intent classification,’ it’s important to note that in the context of LLM-based AI agents, these concepts operate at a much more sophisticated level than in traditional rule-based or pattern-matching systems. Modern LLMs understand language and intent through deep semantic processing, rather than predetermined pathways or simple keyword matching.
Vector Embeddings and Semantic Processing
User intent often lies beneath the surface of their words. Someone asking “Where’s my stuff?” might be inquiring about order status, delivery timeline, or inventory availability. Vector embeddings help bridge this gap by capturing semantic meaning behind queries.
Vector embeddings create a map of meaning rather than matching keywords. This enables your agent to understand that “I need help with my order” and “There’s a problem with my purchase” request the same type of assistance, despite sharing no common keywords.
Disambiguation Strategies
Users often communicate vaguely or assume unspoken context. An effective AI agent needs strategies for handling this ambiguity – sometimes asking clarifying questions, other times making informed assumptions based on available context.
Consider a user asking about “the blue one.” Your agent must assess whether previous conversation provides clear reference, or if multiple blue items require clarification. The key is knowing when to ask questions versus when to proceed with available context. This balance between efficiency and accuracy maintains natural, productive conversations.
Input Processing and Validation
Before formulating responses, your agent must ensure that input is safe and processable. This extends beyond security checks and content filtering to create a foundation for understanding. Your agent needs to recognize entities, identify key phrases, and understand patterns that indicate specific user needs.
Think of this as your agent’s first line of defense and comprehension. Just as a human customer service representative might ask someone to slow down or clarify when they’re speaking too quickly or unclearly, your agent needs mechanisms to ensure it’s working with quality input, which it can properly process.
Intent Classification Architectures
Reliable intent classification requires a sophisticated approach beyond simple categorization. Your architecture must consider both explicit statements and implicit meanings. Context is crucial – the same phrase might indicate different intents depending on its place in conversation or what preceded it.
Multi-intent queries present a particular challenge. Users often bundle multiple requests or questions together, and your architecture needs to recognize and handle these appropriately. The goal isn’t just to identify these separate intents but to process them in a way that maintains a natural conversation flow.
Section 2: Response Generation and Control
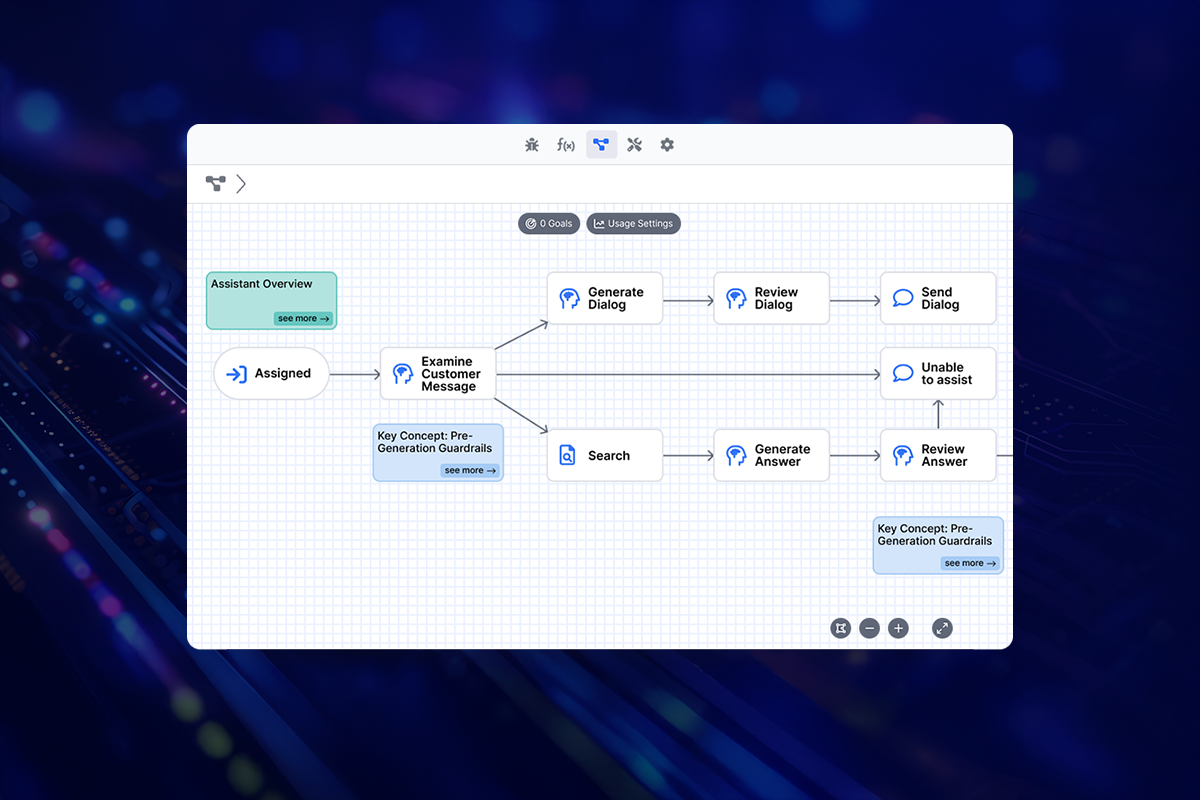
Once we’ve properly understood user intent, the next challenge is generating appropriate responses. This is where many AI agents either shine or fall short. While LLMs excel at producing human-like text, ensuring that those responses are accurate, appropriate, and aligned with your business needs requires careful control and validation mechanisms.
Output Quality Control Systems
Creating high-quality responses isn’t just about getting the facts right – it’s about delivering information in a way that’s helpful and appropriate for your users. Think of your quality control system as a series of checkpoints, each ensuring that different aspects of the response meet your standards.
A response can be factually correct, yet fail by not aligning with your brand voice or straying from approved messaging scope. Quality control must evaluate both content and delivery – considering tone, brand alignment, and completeness in addressing user needs.
Hallucination Prevention Strategies
One of the more challenging aspects of working with LLMs is managing their tendency to generate plausible-sounding but incorrect information. Preventing hallucinations requires a multi-faceted approach that starts with proper prompt design and extends through response validation.
Responses must be grounded in verifiable information. This involves linking to source documentation, using retrieval-augmented generation for fact inclusion, or implementing verification steps against reliable sources.
Input and Output Filtering
Filtering acts as your agent’s immune system, protecting both the system and users. Input filtering identifies and handles malicious prompts and sensitive information, while output filtering ensures responses meet security and compliance requirements while maintaining business boundaries.
Implementation of Guardrails
Guardrails aren’t just about preventing problems – they’re about creating a space where your AI agent can operate effectively and confidently. This means establishing clear boundaries for:
- What types of questions your agent should and shouldn’t answer
- How to handle requests for sensitive information
- When to escalate to human agents
Effective guardrails balance flexibility with control, ensuring your agent remains both capable and reliable.
Response Validation Methods
Validation isn’t a single step but a process that runs throughout response generation. We need to verify not just factual accuracy, but also consistency with previous responses, alignment with business rules, and appropriateness for the current context. This often means implementing multiple validation layers that work together to ensure quality responses, all built upon a foundation of reliable information.
Section 3: Knowledge Integration
A truly effective AI agent requires seamlessly integrating your organization’s specific knowledge, layering that on top of the communication capabilities of language models.This integration should be reliable and maintainable, ensuring access to the right information at the right time. While you want to use the LLM for contextualizing responses and natural language interaction, you don’t want to rely on it for domain-specific knowledge – that should come from your verified sources.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
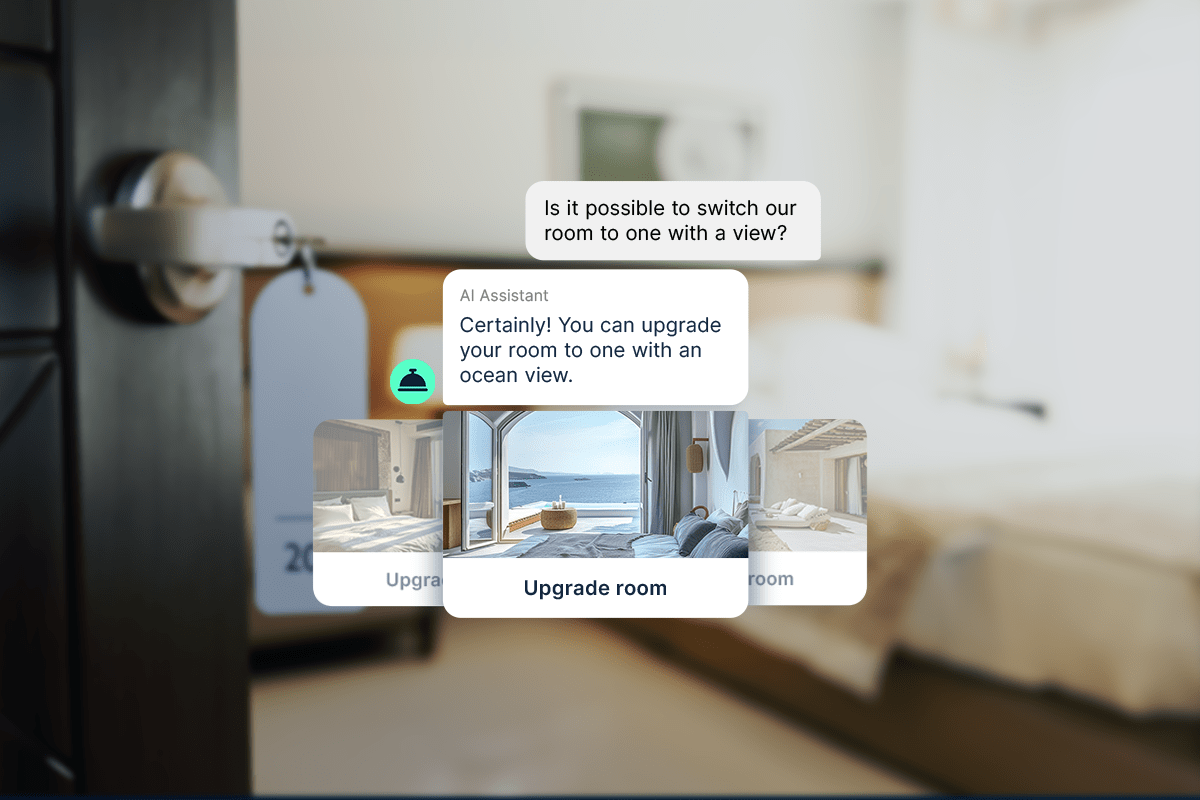
RAG fundamentally changes how AI agents interact with organizational knowledge by enabling dynamic information retrieval. Like a human agent consulting reference materials, your AI can “look up” information in real-time.
The power of RAG lies in its flexibility. As your knowledge base updates, your agent automatically has access to the new information without requiring retraining. This means your agent can stay current with product changes, policy updates, and new procedures simply by updating the underlying knowledge base.
Dynamic Knowledge Updates
Knowledge isn’t static, and your AI agent’s access to information shouldn’t be either. Your knowledge integration pipeline needs to handle continuous updates, ensuring your agent always works with current information.
This might include:
- Customer profiles (orders, subscription status)
- Product catalogs (pricing, features, availability)
- New products, support articles, and seasonal information
Managing these updates requires strong synchronization mechanisms and clear protocols to maintain data consistency without disrupting operations.
Context Window Management
Managing the context window effectively is crucial for maintaining coherent conversations while making efficient use of your knowledge resources. While working memory handles active processing, the context window determines what knowledge base and conversation history information is available to the LLM. Not all information is equally relevant at every moment, and trying to include too much context can be as problematic as having too little.
Success depends on determining relevant context for each interaction. Some queries need recent conversation history, while others benefit from specific product documentation or user history. Proper management ensures your agent accesses the right information at the right time.
Knowledge Attribution and Verification
When your agent provides information, it should be clear where that information came from. This isn’t just about transparency – it’s about building trust and making it easier to maintain and update your knowledge base. Attribution helps track which sources are being used effectively and which might need improvement.
Verification becomes particularly important when dealing with dynamic information. As an AI engineer, you need to ensure that responses are grounded in current, verified sources, giving you confidence in the accuracy of every interaction.
Section 4: Observability and Testing
With the core components of understanding, response generation, and knowledge integration in place, we need to ensure our AI agent performs reliably over time. This requires comprehensive observability and testing capabilities that go beyond traditional software testing approaches.
Building an AI agent isn’t a one-time deployment – it’s an iterative process that requires continuous monitoring and refinement. The probabilistic nature of LLM responses means traditional testing approaches aren’t sufficient. You need comprehensive observability into how your agent is performing, and robust testing mechanisms to ensure reliability.
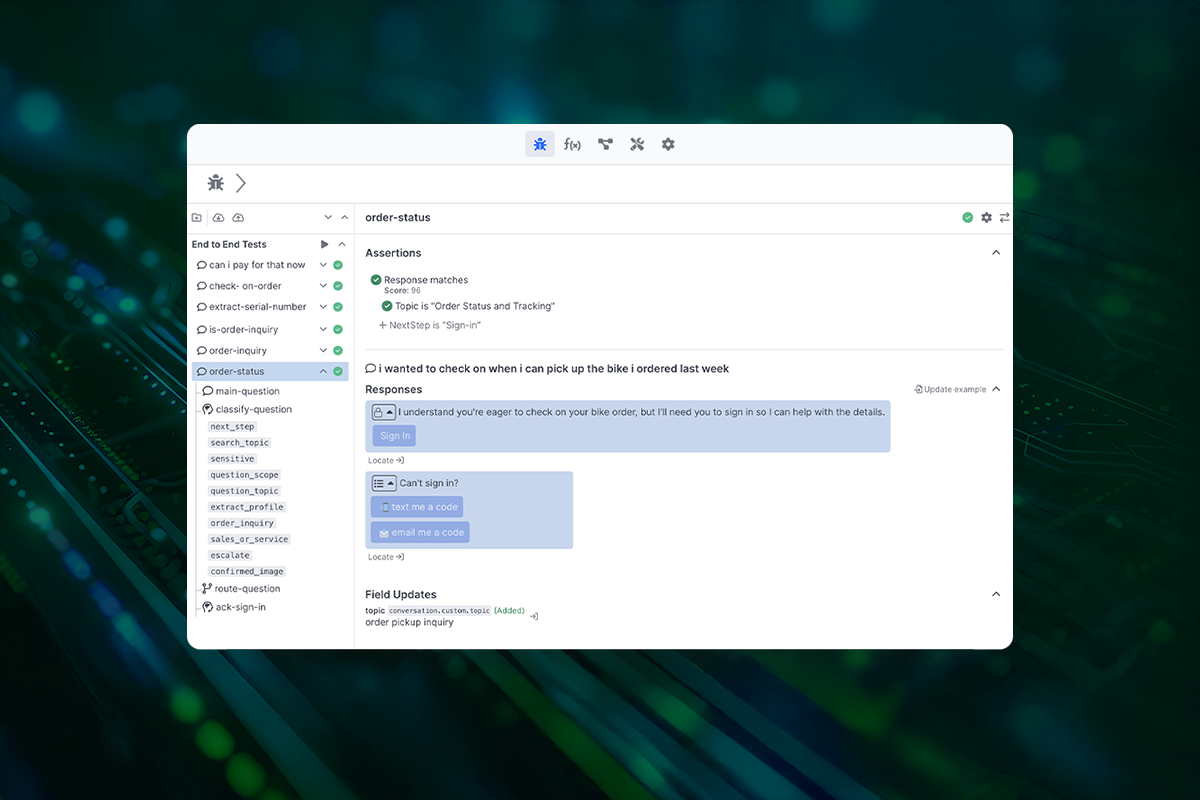
Regression Testing Implementation
AI agent testing requires a more nuanced approach than traditional regression testing. Instead of exact matches, we must evaluate semantic correctness, tone, and adherence to business rules.
Creating effective regression tests means building a suite of interactions that cover your core use cases while accounting for common variations. These tests should verify not just the final response, but also the entire chain of reasoning and decision-making that led to that response.
Debug-Replay Capabilities
When issues arise – and they will – you need the ability to understand exactly what happened. Debug-replay functions like a flight recorder for AI interactions, logging every decision point, context, and data transformation. This visibility lets you trace paths from input to output, simplifying issue identification and resolution. This level of visibility allows you to trace the exact path from input to output, making it much easier to identify where adjustments are needed and how to implement them effectively.
Performance Monitoring Systems
Monitoring an AI agent requires tracking multiple dimensions of performance. Start with the fundamentals:
- Response accuracy and appropriateness
- Processing time and resource usage
- Business-defined KPIs
Your monitoring system should provide clear visibility into these metrics, allowing you to set baselines, track deviations, and measure the impact of any changes you make to your agent. This data-driven approach focuses optimization efforts on metrics that matter most to business objectives.
Iterative Development Methods
Improving your AI agent is an ongoing process. Each interaction provides valuable data about what’s working and what’s not. You want to establish systematic methods for:
- Collecting and analyzing interaction data
- Identifying areas for improvement
- Testing and validating changes
- Rolling out updates safely
Success comes from creating tight feedback loops between observation, analysis, and improvement, always guided by real-world performance data.
Section 5: Advanced Agent Behaviors
While basic query-response patterns form the foundation of AI agent interactions, implementing advanced behaviors sets exceptional agents apart. These sophisticated capabilities allow your agent to handle complex scenarios, maintain goal-oriented conversations, and effectively manage uncertainty.
Task Decomposition Strategies
Complex user requests often require breaking down larger tasks into manageable components. Rather than attempting to handle everything in a single step, effective agents need to recognize when to decompose tasks and how to manage their execution.
Consider a user asking to “change my flight and update my hotel reservation.” The agent must handle this as two distinct but related tasks, each with different information needs, systems, and constraints – all while maintaining coherent conversation flow.
Goal-oriented Planning
Outstanding AI agents don’t just respond to queries – they actively work toward completing user objectives. This means maintaining awareness of both immediate tasks and broader goals throughout the conversation.
The agent should track progress, identify potential obstacles, and adjust its approach based on new information or changing circumstances. This might mean proactively asking for additional information when needed or suggesting alternative approaches when the original path isn’t viable.
Multi-step Reasoning Implementation
Some queries require multiple steps of logical reasoning to reach a proper conclusion. Your agent needs to be able to:
- Break down complex problems into logical steps
- Maintain reasoning consistency across these steps
- Draw appropriate conclusions based on available information
Uncertainty Handling
Building on the flexible frameworks established in your initial design, advanced AI agents need sophisticated strategies for managing uncertainty in real-time interactions. This goes beyond simply recognizing unclear requests – it’s about maintaining productive conversations even when perfect answers aren’t possible.
Effective uncertainty handling involves:
- Confidence assessment: Understanding and communicating the reliability of available information
- Partial solutions: Providing useful responses even when complete answers aren’t available
- Strategic escalation: Knowing when and how to involve human operators
The goal isn’t eliminating uncertainty, but to make it manageable and transparent. When definitive answers aren’t possible, agents should communicate limitations while moving conversations forward constructively.
Building Outstanding AI Agents: Bringing It All Together
Creating exceptional AI agents requires careful orchestration of multiple components, from initial planning through advanced behaviors. Success comes from understanding how each component works in concert to create reliable, effective interactions.
Start with clear purpose and scope. Rather than trying to build an agent that does everything, focus on specific objectives and define clear success criteria. This focused approach allows you to build appropriate guardrails and implement effective measurement systems.
Knowledge integration forms the backbone of your agent’s capabilities. While Large Language Models provide powerful communication abilities, your agent’s real value comes from how well it leverages your organization’s specific knowledge through effective retrieval and verification systems.
Building an outstanding AI agent is an iterative process, with comprehensive observability and testing capabilities serving as essential tools for continuous improvement. Remember that your goal isn’t to replace human interaction entirely, but to create an agent that handles appropriate tasks efficiently, while knowing when to escalate to human agents. By focusing on these fundamental principles and implementing them thoughtfully, you can create AI agents that provide real value to your users while maintaining reliability and trust.
Ready to put these principles into practice? Do it with AI Studio, Quiq’s enterprise platform for building sophisticated AI agents.